AM5 vs LGA 1700: Which is a better platform?
Here we will analyse the differences between the platforms of AMD and Intel respectively, to determine which is objectively better.

WePC is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Prices subject to change. Learn more
AM5 vs LGA 1700, which is better? AMD and Intel have been at war with each other for years now, with each company constantly trying to one-up the other in terms of manufacturing a better CPU.
Many articles and videos have been dedicated to examining AMD and Intel’s CPUs to determine which is better. But it’s less common to see comparisons between the motherboard platforms those very CPUs belong to. Here’s our AM5 vs LGA 1700 article.
Now read: AMD Vs Intel
There are a few things we need to understand before we go off comparing motherboards and getting onto the intricacies surrounding them.
What is a motherboard?
We’re sure you know what a motherboard is, but we’ll go over it anyway for those who might not.

A motherboard is a printed PCB that sits at the core of a computer, connecting all the PC components together and allowing them to communicate with one another. The motherboard is laced with thin layers of copper known as traces, these tracers carry signals to and from each of the PC components connected to it.
The motherboard itself is comprised of multiple components, the most notable of which are the Socket, chipset, and I/O.
Socket
The socket is probably one of the most integral components of the motherboard, the socket is where the CPU sits and is either based on an LGA (land grid array) or PGA (pin grid array) configuration.
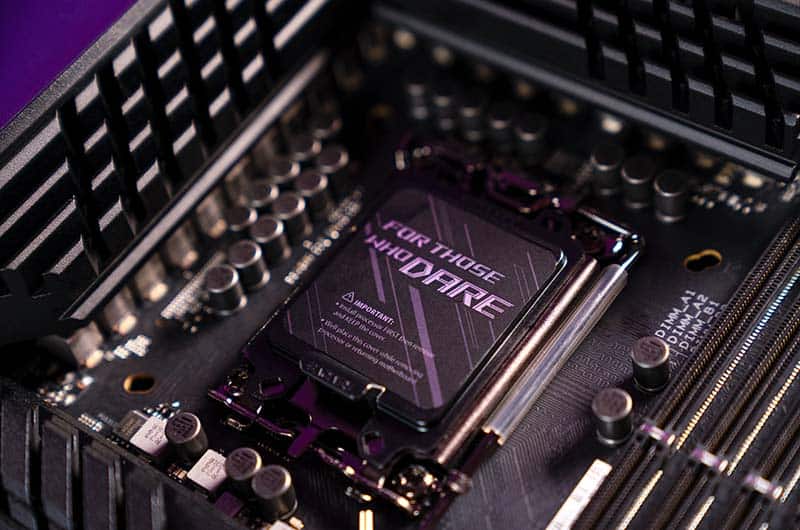

The socket is where the CPU connects to the motherboard and is also the anchor point in which CPU coolers are securely connected to both CPU and motherboard. It’s one of the most volatile motherboard components, yet it’s also one of the strongest physically.
The socket has PCI lanes, connectors, and tracers that both feed and receive data. One of the strongest connections on a motherboard is between the socket and RAM. The reason for this is that the RAM is the component that feeds the CPU instructions from computer programs, it’s also where the CPU stores its completed computations.
Chipset
The chipset is the area of the motherboard that controls almost everything, but its primary job is to control the communication between your CPU, RAM, and other components and peripherals. The chipset also determines how many high-speed connection devices such as USBs your motherboard can support at any given time.
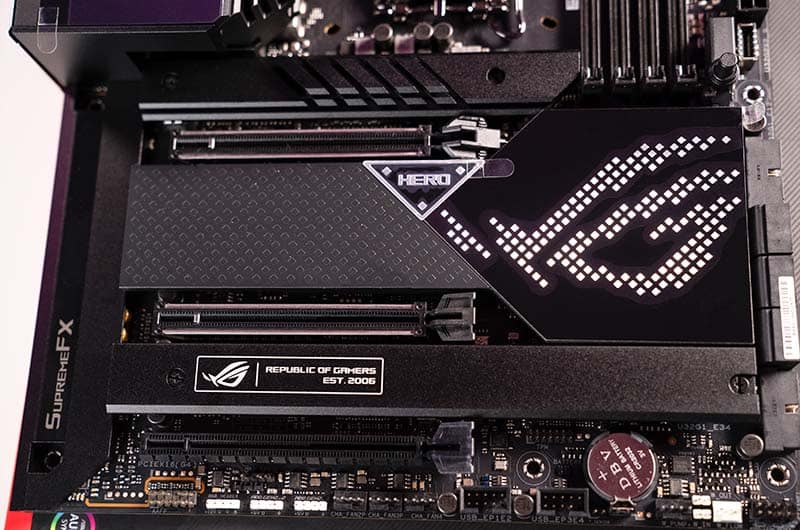

Chipsets are usually composed of one or more chips (two on the X670 and X670-E motherboards) that feature controllers for not just hardware devices, but more commonly used peripheral devices too, such as keyboards and mice.
If you know anything about motherboards you will have heard the terms, ‘X670, Z690, B550’, and so on – these are the chipsets. The names can seem a little confusing at first but all you need to know is that they follow a hierarchy for both AMD and Intel processors, and the higher the number the better the chipset and the more it will support (for the most part).
I/O
I/O is pretty simple, it stands for input/output. And it refers primarily to the connectivity on the back of the motherboard. Without this connectivity, you wouldn’t be able to control your PC or ask it to do literally anything.
I/O is how your mouse works, headphones work, and front panel USB connectors work. If it’s connected to your PC, I/O is probably at play somewhere allowing the communication outside of the PC to the device.
AM5 vs LGA 1700: what’s the difference?
Now you know what a motherboard is on a fundamental level, it’s time to explore the differences between each platform. AM5 vs LGA 1700.
AM5
What is AM5? Good question, since it isn’t currently out yet, let us explain.

AM5 is the brand new socket from AMD to set its new Zen 4 CPUs. Dubbed the 600 series AM5 motherboards, they were announced at Computex 2022 and will release sometime in the Fall of this year.
The New motherboards are set to feature a whole host of new technology including DDR5 support, 24 ultrafast PCIe lanes capable of gen 5 speeds, and 14 super speed USB ports, boasting 20GB/s speeds – just to name a few.
Not just that, AMD is moving from the PGA (Pin grid array) to the LGA (Land grid array) for a “better connection between CPU and motherboard”. This also helps keep the cost of CPU manufacturing down, as the process becomes significantly easier for AMD using this standard.
Contrarily, though, it also makes the manufacturing of motherboard sockets more difficult for AMD’s partners. But this configuration has worked for Intel for a long time, we don’t see how it won’t for AMD.
There are three chipsets for AM5 that have been announced, these are the X670E, X670, and B650.
- X670E (extreme) is the best of the best, featuring all the connectivity powered by the latest and fastest technology – DDR5, PCIe 5 – and the most extreme overclocking potential.
- X670 will feature some PCIe gen 5 connectivity, but not all PCIe or M.2 slots. X670 will also most likely have less connectivity, but will still feature strong overclocking potential
- B650 is the budget option, being a more bare-bones motherboard with less connectivity. The perfect balance of price point and capability – featuring all the connectivity that AM5 has to offer, but none or much less of the overclocking capabilities.
That’s about all we know on AM5, but we’ll keep the information coming as we learn it.
LGA 1700
Unlike AM5, we know plenty around LGA 1700 as it’s currently on the market.
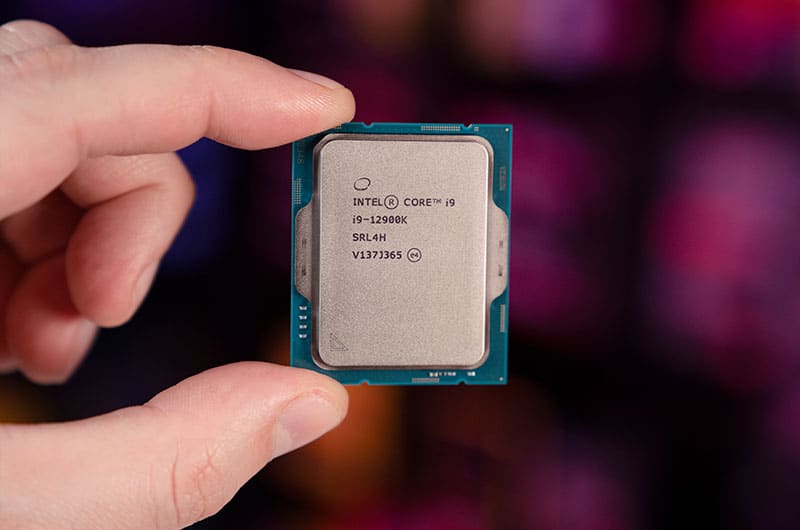

LGA 1700 was released alongside Intel’s 12th generation Alder Lake CPUs. LGA 1700 featured all the latest bells and whistles, such as PCIe Gen 5, DDR5 RAM support, and WIFI 6E.
Specifically, The Z690 offers the same USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 design which doubled the performance of the previous generation of USB 3.2 Gen 2. Up to 20Gbps ultra-fast data transfer while connecting to USB 3.2 compliant peripherals.
Not only that, the Z690 chipset of LGA 1700 offers 16 PCIe 5.0 lanes and 2 x 8 PCIe 4.0 lanes should you be running in SLI or crossfire.
LGA 1700 is the most advanced Intel socketed motherboard set to date, leaving AMD in the dust in terms of staying up to date. This must be why it feels like there’s far less to mention, as it’s AMD that hasn’t seen a proper update for well over 5 years.
There will be an update to LGA 1700 as Intel launches its 13th gen CPUs, we expect to see 700 series LGA 1700 motherboards hot on the market at some point in the second half in 2024. This is because Intel promised to keep LGA 1700 in use for at least three years. The 700 series motherboards will mark the second generation of LGA 1700 motherboards.
There are three mainstream chipsets available on the LGA 1700 platform currently.
- Z690 is the best of the best that Intel has to offer currently, featuring all the technology and power conceivable a year ago. DDR5, PCI-e gen 5 (no storage), and all the overclocking support you could ever need for these power-hungry CPUs.
- B660 is a middle ground between the three chipsets, it features most of the connectivity of the Z690 chipset, bar a few creature comforts. But only features overclocking potential on the RAM. The B660 shouldn’t hurt CPU performance much, if at all.
- H610 is the bottom-tier budget chipset, which features NO overclocking support and very limited connectivity. However, as a result, the H610 is the best value for money when it comes down to it. Funnily enough, the H610 is the only beard that does not support a PCI-e gen 4 Processor PCI Express configuration.
AM5 vs LGA 1700: Technology
Fundamentally, they accomplish the same thing. They’re both motherboard sockets and the bases of both companies’ chipsets.
AM5 will be a little newer, however, at least until Intel plays catch up when it releases its 700 series motherboards. The most notable difference is the PCI-e Gen 5 storage. Currently, AM5 is the only motherboard set to carry this updated PCI-e SSD generation. Specifically on its X670E, Z670, and B650 chipsets.
AMD natively supports faster RAM speed than Intel and this has always been the case since Ryzen core communication speed is directly associated with RAM speed.
AM5 will be more up-to-date, at least until Intel releases its 700 series motherboards. But with AMD moving to LGA and launching the first major motherboard technology update in over 5 years, there’s bound to be some teething issues.
So beware when purchasing an AM5 motherboard upon launch. We have every faith in Zen 4 and AM5 don’t get us wrong, we’re merely suggesting you give AMD time to iron out the issues.
CPU

The biggest difference between the two is the CPU you choose to put in your rig, you obviously can’t put a Ryzen CPU in an Intel board. So it’s the CPU that should be mainly influencing your decision.
We have Intel 12th gen and Zen 4 articles for more in-depth information. But generally, Intel has single-core performance down, beating every AMD processor in single-core loads, despite its lower IPC.
AMD holds the title for best multi-core performance, even though some of Intel’s newest CPUs beat the older Ryzen flagships, you have to remember that AMD is a generation behind at this point. And if Intel manages to release its CPUs before Zen 4 launches, then AMD will be two whole generations behind – yet AMD’s CPUs still compete.
Check out AMD Vs Intel for more information on this.
Final word
In general, both AM5 and LGA 1700 are great platforms, but it should be the CPUs that are influencing your decision. As CPUs have a much greater impact on system performance and usability than a motherboard does. Now, if you were to ask us what CPU is better, then that would probably be a whole different story.
But that will have to wait until the release of AM5 and Zen 4 for us to make a proper decision. We hope you enjoyed our AM5 vs LGA 1700 article, and we will update it as we get more information on the upcoming technology.