What Is FreeSync? Everything You Need To Know
An in-depth explanation of AMD's FreeSync and how it improves your overall gaming performance

WePC is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Prices subject to change. Learn more
What is FreeSync? Historically, monitors were plagued with the screen artifact that is better known as screen tear – a visual artifact that is characterized by two (or more) frames being displayed at the same time. This annoying screen defect not only reduces overall smoothness and immersion when playing your favourite titles, but also put you at a clear disadvantage when playing competitive games at higher levels.
Fortunately, GPU manufacturers clocked onto this some time ago now and introduced variable refresh rate technology that enables your GPU and monitor to communicate and reduce said artifacts.
In today’s article, we’ll be answering some of the big questions around AMD’s Freesync – looking at how it performs, what the benefits are, and how it compares to Nvidia’s G-Sync.
So, with plenty to get through, let’s dive into it!
What Is FreeSync
FreeSync is AMD’s entry-level variable refresh rate technology. It was released back in 2014 to help reduce the screen tearing that would occur when your monitor’s refresh rate wasn’t synced with your GPU’s frame rate output. Confused? Let me explain.
A monitor’s refresh rate is measured in hertz and lets us know how many times your display can refresh itself every second. A GPU, on the other hand, is a graphics processor that renders frames and sends them to the monitor. In an ideal world, we want the GPU to render the exact number of frames (FPS) that the monitor can refresh every second. So, a monitor that refreshes itself 75 times per second (75 Hz), will function at its most efficient when fed 75 frames per second by the GPU. But what happens when this synchronization doesn’t happen – well, screen tear happens.
As you probably know, many PC setups will struggle to hold a fixed number of frames when playing more demanding, modern titles. We often see large variations in FPS depending on what game we’re playing, how graphically demanding the game is, and what screen resolution we’re using. In these scenarios, whether it’s two frames being displayed at once or just general gameplay stuttering, we’ll often see some form of screen tear occur.
Fortunately, that’s where FreeSync lends a helping hand. The variable refresh rate technology from AMD allows your GPU to control how often your monitor refreshes itself per second – synchronizing the monitor’s refresh rate with the number of FPS you’re getting at any given time.
Obviously, this comes with its limitations. A monitor with a refresh rate of 60Hz will only be able to support a variable refresh rate of up to 60 frames per second. In this instance, you’ll have to cap your FPS to 60 for the best results. That being said, if your PC struggles to push 60+ FPS, FreeSync will reduce the monitor’s refresh rate (down to 9 frames per second) to match your frame rate – creating a much smoother, tear-free experience.
Check out our complete guide on refresh rates here.
FreeSync pros & cons
Like any major technology, FreeSync comes with a host of pros and cons that should be considered before diving into your next monitor purchase.
Below, we’ll outline some of the major pros and cons you should know when it comes to using FreeSync:
Pros
License-free: Unlike G-Sync, which uses a proprietary module in each G-Sync monitor, FreeSync is based on an open source standard. This means that FreeSync monitors can be manufactured with fewer costs.
Reduces screen tear: FreeSync is a custom-designed technology that matches your framerate to the refresh of the monitor. The main benefit of this is to reduce the annoying screen artifact known as screen tear.
Cons
Not all FreeSync monitors are G-Sync compatible: While the majority of the FreeSync monitors in today’s market are G-Sync compatible, that isn’t the case for all models. Some FreeSync monitors simply haven’t been certified for NVIDIA GPUs, meaning you will need an AMD graphics card to use FreeSync on some monitors.
Not as consistent as G-Sync: Consistency can be problematic with FreeSync monitors, with refresh rate ranges varying from panel to panel. When compared to G-Sync alternatives, there is a noticeable difference in consistency.
What components do I need for FreeSync?
So, to actually use FreeSync you’ll first need a compatible AMD graphics card or APU (AMD’s all-in-one processor that offers built-in graphics). Fortunately, almost every new GPU that comes out of the AMD warehouse will offer FreeSync compatibility – no matter what budget or price category. However, if you’re unsure, feel free to check the product specifications first.
Secondly, you’ll need a compatible monitor or TV that supports VESA’s adaptive-sync – a technology that is utilized in almost every modern panel. Adaptive-sync is driven by a built-in scaler board that also powers the OSD, overdrive settings, backlight controls, and everything else that your monitor offers. Without it, your monitor and GPU wouldn’t be able to communicate with each other.
Alongside a compatible monitor and GPU, you’ll also need to utilize the correct input cable. DisplayPort 1.2a was added to the variable refresh rate support list back in 2014, with HDMI 2.1 following by early 2017. These are also essential requirements when using FreeSync technology.
And that’s pretty much it. Unlike G-sync monitors that require a number of additional extras to support Nvidia’s variable refresh rate, FreeSync monitors are fairly straightforward. However, don’t think they don’t go through the same meticulous certification process as their green counterparts.
According to AMD, each panel that offers FreeSync support goes through a custom certification process which ensures only the smoothest, tear-free, low latency gaming experience possible. Just like Nvidia, only the best gaming monitors make the FreeSync cut.
How to enable FreeSync
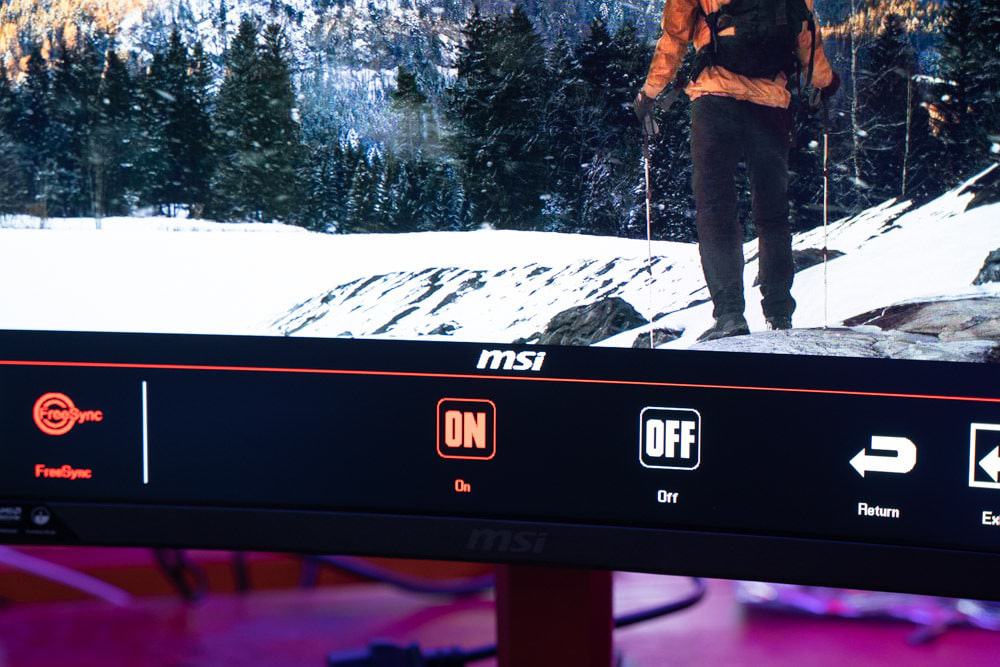
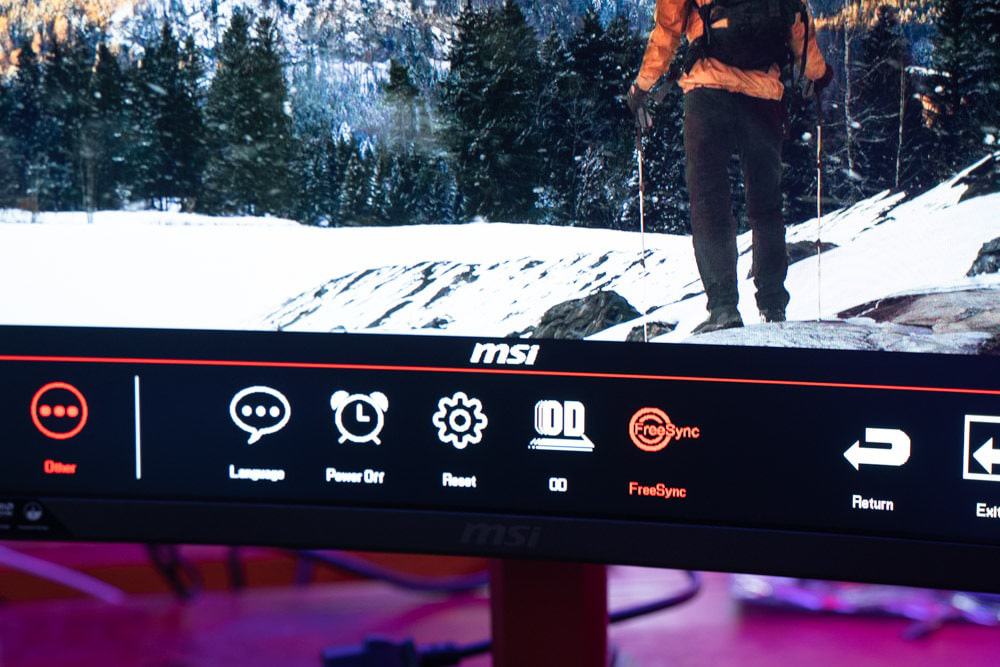
Turning on FreeSync when using a compatible monitor is an extremely easy task. First off, start by entering your monitor’s OSD. Nine times out of ten, your monitor will have a variable refresh rate option that allows you to enable/disable FreeSync. Making sure FreeSync is enabled in your monitor is the first thing you should do.
Secondly, be sure to have all the latest drivers for your AMD GPU. To do this, you can download the latest drivers from the AMD website. The installer will get the latest drivers that are required to enable FreeSync compatibility. You can also manually enter the GPU or APU in AMD’s ‘Manually select your driver’ tool – just remember to select the correct version of Windows.
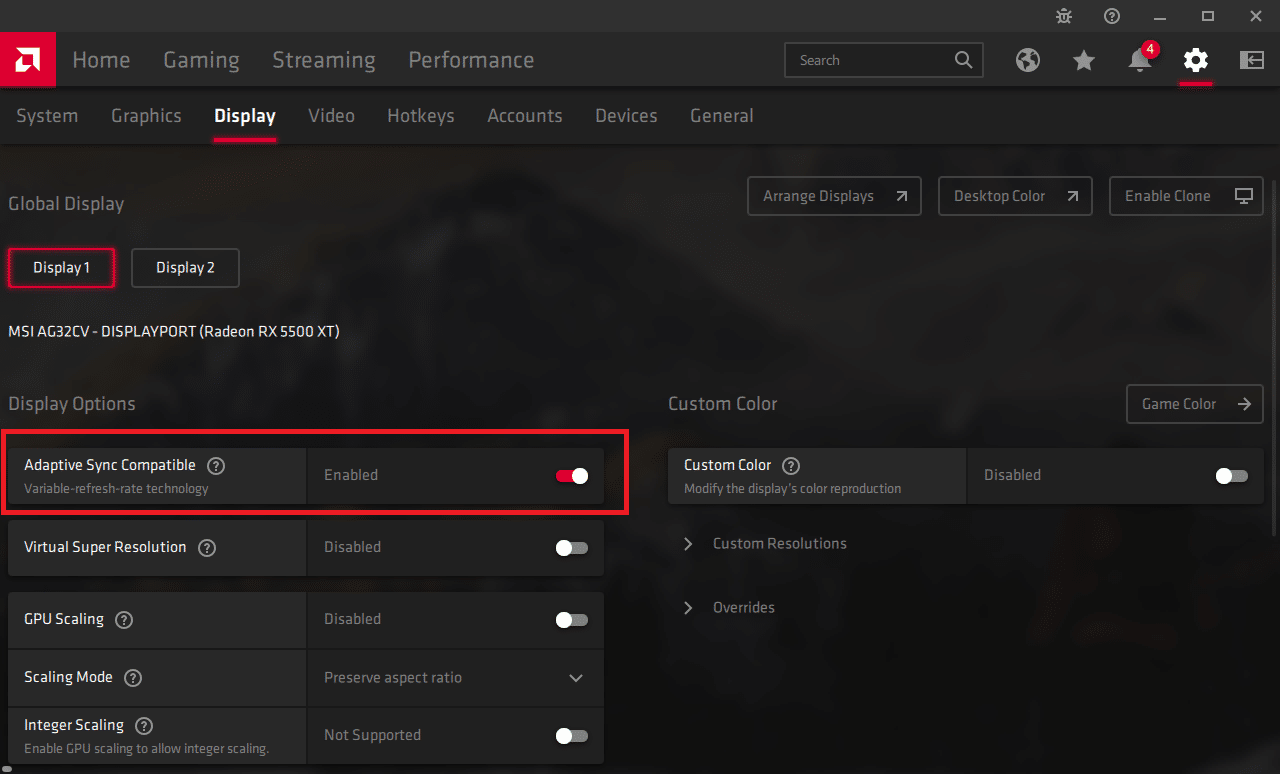
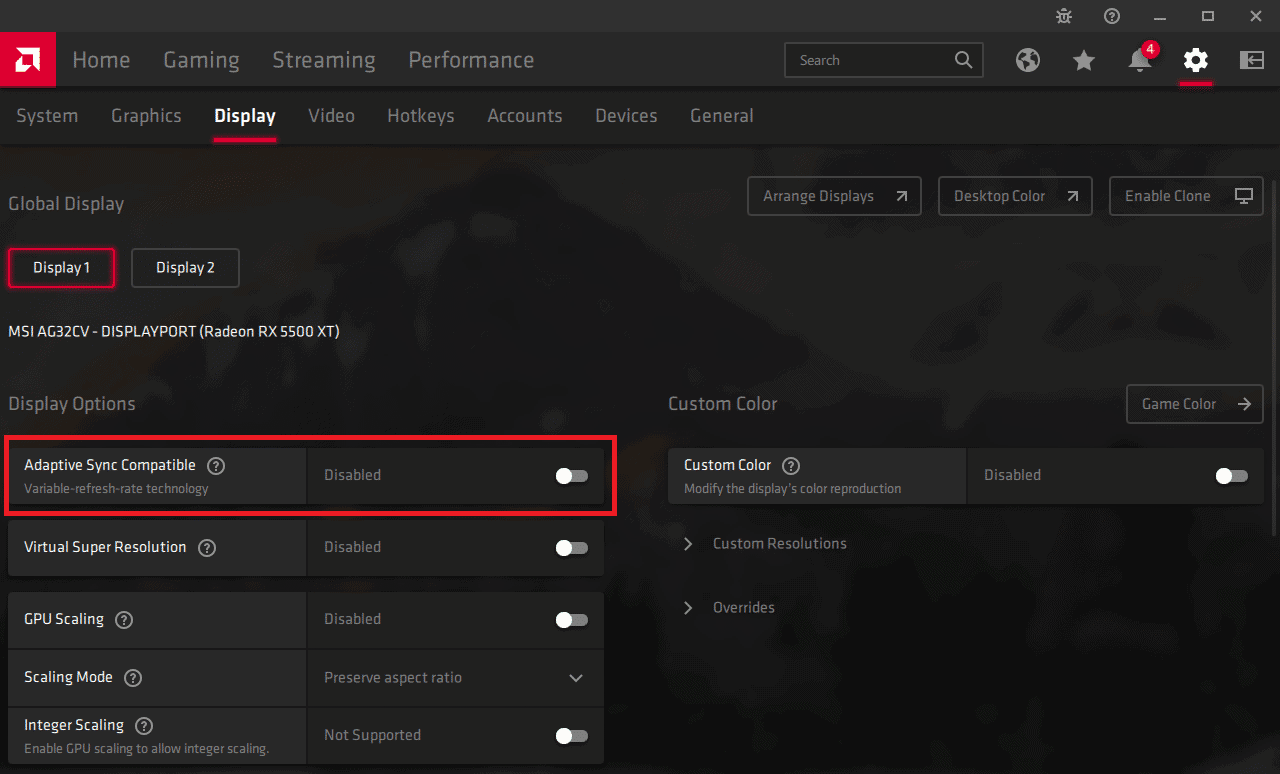
When the latest drivers have been installed and you’ve restarted your PC, start by opening the AMD Radeon software suite. You can do this by right-clicking the desktop and selecting ‘AMD Radeon Software’ from the available options. Once inside, click the ‘Display’ tab from the top navigation bar and locate the ‘Display Options’ portion of the tab.
Inside this section, you’ll see the toggle setting for AMD FreeSync. Simply click the toggle bar to ‘On’ and that’s all there is to it.
What Is FreeSync Premium & FreeSync Premium Pro?
Like G-sync, FreeSync has a number of different standards to choose from. Each of the standards offers a different set of benefits that increase as you reach the more premium variants.
FreeSync Premium is the next step up AMD’s variable refresh rate ladder, providing at least a 120Hz refresh rate at minimum FHD resolution. Alongside better support for FHD resolutions at faster refresh rates, FreeSync Premium also offers support for LFC – low framerate compensation. This technology actually allows FreeSync to continue working even when the framerate drops below the minimum refresh rate of the display. That means monitors that offer FreeSync Premium will have the ability to utilize the full 9-240hz VRR range that FreeSync provides – ensuring smooth gameplay throughout.
One further step up the ladder sees us reach FreeSync Premium Pro – a more advanced version of both the basic and the premium iterations. Like G-sync Ultimate, FreeSync Premium Pro (previously known as FreeSync 2 HDR) offers support for HDR capabilities and game support. It also brings 120Hz min refresh rate at FHD resolution, LFC, tear-free, low flicker, and low latency in both SDR and HDR to the table too.
Is your monitor FreeSync certified?
If you’ve had your monitor for a while now, you may not be aware of its VRR (variable refresh rate) compatibility. Fortunately, there’s a pretty easy way of checking whether or not your monitor is FreeSync or G-Sync – or neither.
The first, and easiest way to check whether your monitor is FreeSync compatible is to simply head on over to AMD’s official FreeSync monitor page where it clearly outlines every monitor with FreeSync support.
If you aren’t sure what the model number of your monitor is, you can also check inside your OSD (on-screen display). If you navigate to the picture/game settings, you’ll likely be given an option to enable FreeSync or G-Sync.
Alternatively, G-Sync monitors usually showcase some form of branding on the front of the monitor, indicating it utilizes a proprietary G-Sync module.

Are FreeSync monitors G-Sync compatible?
One of the big questions we get asked regarding FreeSync monitors is, do they offer G-sync compatibility?
The official answer is, some do and some don’t. You’ll be able to find out whether your FreeSync monitor is G-Sync compatible by checking the user manual or contacting the manufacturer of the monitor via their social channels.
However, the less official answer is, most likely. Back in 2019, NVIDIA announced that a number of FreeSync monitors had been officially certified as being able to run G-Sync systems. This was only possible thanks to a software-based version of G-Sync solution, where users would have to download and install the software onto a system using a FreeSync monitor.
Since then, a tonne of FreeSync monitors has been certified for usage with G-Sync systems. If you want to see whether your monitor is included in that list, check out NVIDIA’s official G-Sync compatible monitor list here.
Final Thoughts
So, there you have it guys, everything you need to know about FreeSync. Hopefully, this article has answered the big question many people have on AMD’s VRR technology (what is FreeSync?). We’ve tried to answer exactly what FreeSync is in the easiest possible way, making the entire process of using and understanding this technology a little more digestible.
If you have any questions regarding AMD’s FreeSync, feel free to drop a comment in the section below and we’ll answer them as soon as we can!